Aligni’s quality control system uses usage-based billing. For additional information, please visit our Usage Billing page.
The goal of the quality control (QC) system is to ensure that materials, components, and finished products meet the required quality standards before they move to the next phase of production or distribution. It helps maintain product integrity, reduce waste, and enhance customer satisfaction by preventing defective materials from entering the supply chain.
Aligni’s quality control record (QCR) manages the workflow and documents the results of the evaluation, assessment, decisions, and disposition of material that undergoes a quality control process.
There are a number of settings available to organizations to customize the workflow for the products you sell, the processes you follow, and the analytics you need. These settings are described at the end of this page.
We recommend that your team review the process and try to configure your settings soon so that your data is as consistent as possible.
Workflow Summary
Aligni’s quality control workflow is designed to reflect the most common material review workflows and enables records capture for vendor performance review and root cause analytics. The workflow is designed to accomplish three primary objectives:
- Document the process of quality control for audit purposes as part of a quality management process;
- Provide a venue for team collaboration and reliable, accountable communication; and
- Catalog condition assessments, root cause assessments, and material routing for the purposes of data analytics and process measurements.
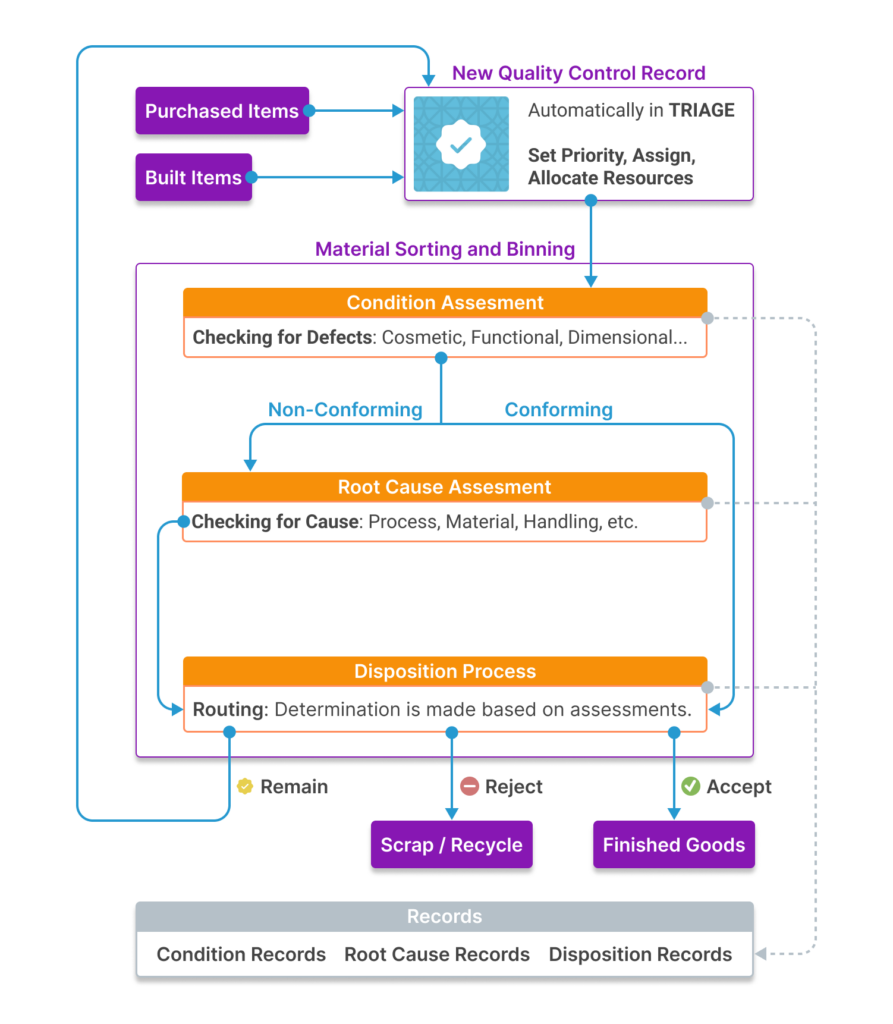
The overall workflow for material sent through the quality control process is summarized in the following sections. The full process of quality control often involves personnel from diverse areas of expertise and responsibility. Aligni’s QCR is designed to streamline the workflow, facilitate team collaboration, improve record keeping, and increase overall efficiency.
Triage
Once material (an inventory unit) is introduced to the QC process, a quality control record is created to represent the journey to eventual exit from QC. The presence of an active QCR restricts what can be done with the material. The triage stage allows managers to prioritize, assign relevant tasks to the QCR, and allocate resources.
Condition Assessment
Once activated, the material is then inspected and assessed. This stage varies greatly depending on the material, the organization, and quality control requirements but typically involves manually or automatically comparing the material to reference standards in one or more categories such as cosmetic, functional, dimensional, etc. If any defects are found, they are graded. Lots of inventory are often sorted or binned at this stage as well.
Each organization can define their own dimensions for condition assessment as well as the severity levels applicable to their requirements.
Root Cause Assessment
Root cause assessment is important to help determine the next stage in the journey and is often associated with the binning. Recording of root causes is helpful for quality analytics and vendor performance measurements. Each organization can define their own set of root cause assessments and additional labels within each to provide further granularity for analytics.
Disposition
After assessment has been completed, the disposition of each bin within the lot is determined and the material moves along to the next stage of the journey. Material may be accepted (even with minor defects), reworked, repaired, or scrapped. This might involve additional quality control stages, acceptance into the supply chain, or rejection.
Closure
When the QCR is closed, inventory transactions are performed based on the selected dispositions of each bin. Inventory is either accepted, rejected, or selected to remain in the quality control process for additional handling. New QCRs are created in the latter case.
Collaboration Features
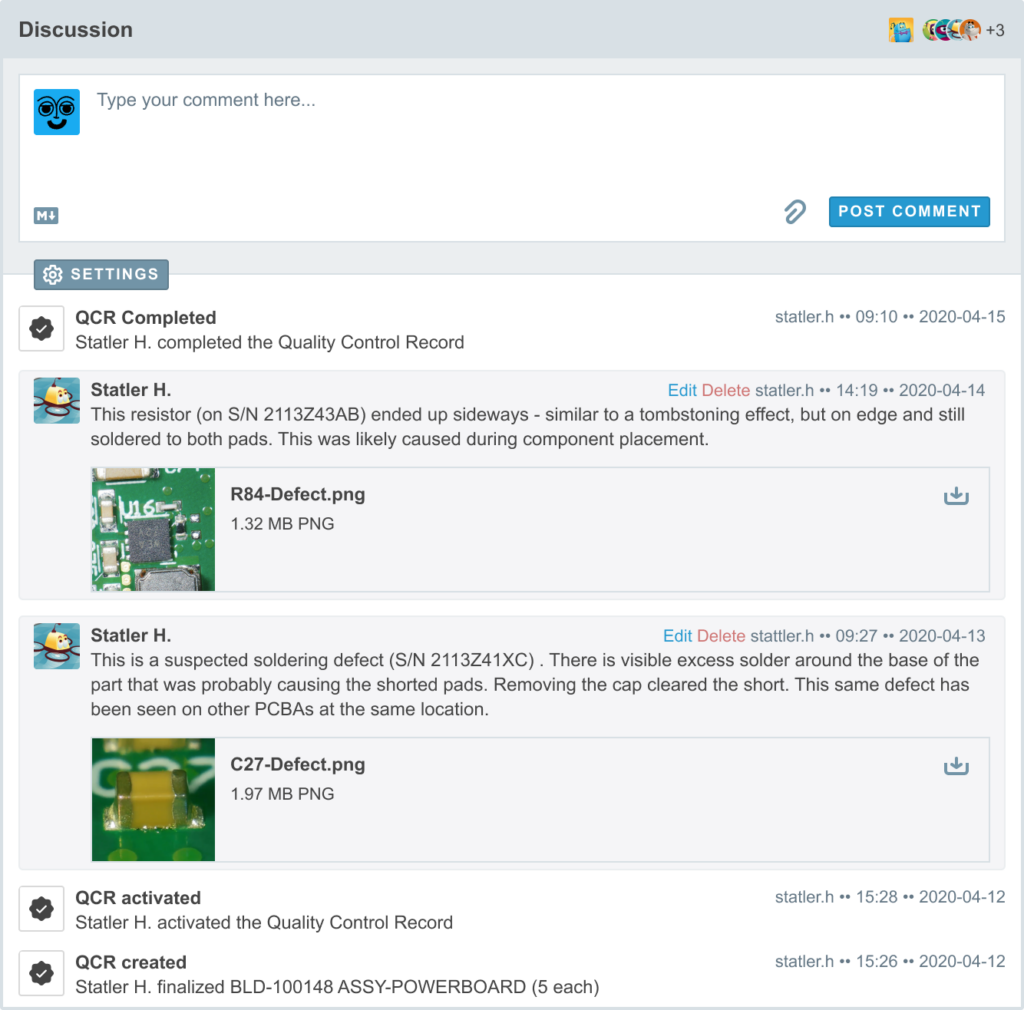
Quality Control Records include a record-specific discussion for team collaboration and record keeping. These discussions support common features such as at-mentions, subscribe / unsubscribe capability, attachments, and notifications to help your team coordinate efficiently. Additionally, relevant events are posted to the activity timeline for context.
Activity Stages
While a QCR is in the “active” state, a configurable secondary attribute called “stage” is available to help the team understand what actions have been performed. This additional parameters allows the quality team to organize the process and responsibility of a large number of QCR. For more information, please see the section below titled Active Quality Control Records.
Discussions
QCR also support Aligni Discussions for integrated team collaboration and activity streams. Discussions help support the quality control process when multiple individuals from different teams need to work together to solve problems.
Inventory Management
Quality control is very closely associated with inventory management and directly impacts the behavior of inventory within Aligni. Quarantine zones within each warehouse may be defined as areas where quality control takes place. All of the quarantine zones within your organization are collectively known as quarantine.
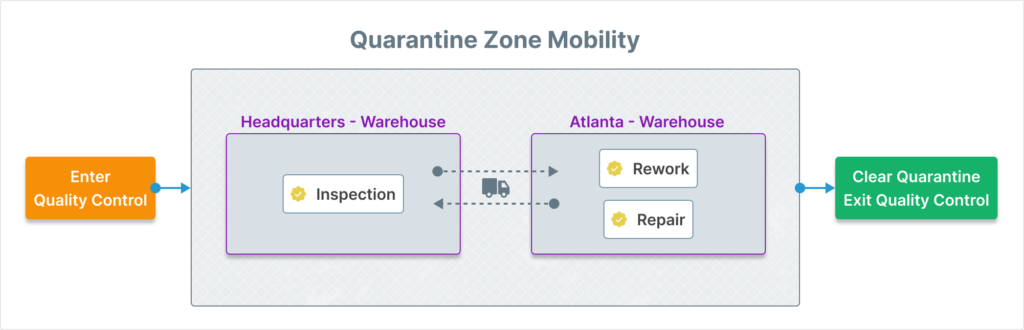
The rules regulating inventory movement into and out of quality control are as follows:
- There is a 1:1 correspondence between a Quality Control Record (QCR) and an inventory unit. Every inventory unit within quality control has an associated QCR. And every active QCR has exactly one inventory unit associated with it.
- To enter quality control, a QCR must be created and attached to the inventory unit. Simultaneously, inventory unit must be moved to a defined quarantine zone.
- To exit quality control, the QCR must be closed. This process detaches from the inventory unit and may have other outcomes such as the movement of the inventory unit out of a quarantine zone.
- Within quarantine (the collective of all quarantine zones), inventory attached to a QCR is able to move freely — even to other warehouses.
- Inventory within quarantine is non-nettable. This means that it is not available for builds and will not satisfy material shortages on the MSR.
Many actions that impact an inventory unit such as moving or splitting, are limited only to accounts with quality control permissions. For example, the actions for moving and splitting an inventory are not available on the inventory tab for the item. Instead, these actions are only available within the quality control record.



